- MENU
- HOME
- SEARCH
- WORLD
- MAIN
- AFRICA
- ASIA
- BALKANS
- EUROPE
- LATIN AMERICA
- MIDDLE EAST
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Argentina
- Australia
- Austria
- Benelux
- Brazil
- Canada
- China
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- India
- Indonesia
- Ireland
- Israel
- Italy
- Japan
- Korea
- Mexico
- New Zealand
- Pakistan
- Philippines
- Poland
- Russia
- South Africa
- Spain
- Taiwan
- Turkey
- USA
- BUSINESS
- WEALTH
- STOCKS
- TECH
- HEALTH
- LIFESTYLE
- ENTERTAINMENT
- SPORTS
- RSS
- iHaveNet.com: Stock Markets
By Felix Richter (Statista)
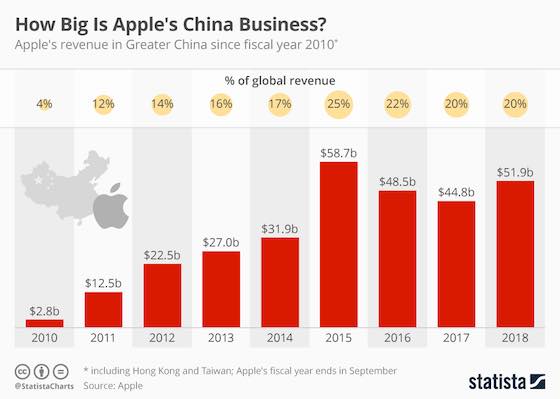
How Big Is Apple's China Business?
This chart shows China's impact on Apple's global sales.
Having gone from major growth driver to weak spot before, Apple's Greater China business has once again proven to be the proverbial banana skin on the company's road to another record-breaking holiday quarter.
When Apple CEO Tim Cook announced a downward revision of the company's revenue guidance for the December quarter, he attributed "most of our revenue shortfall to our guidance, and over 100 percent of our year-over-year worldwide revenue decline" to iPhone, Mac and iPad sales across Greater China. In his statement, Cook blames China's recent economic slowdown and rising trade tensions between the United States and China for Apple's lackluster performance in the country but the high prices of Apple's latest flagship iPhone models may have also played a part.
As the chart above shows, Apple's China business has grown nearly twentyfold since the company entered the Chinese phone market in 2010. In Apple's fiscal year 2018 (which ended September 27), Greater China accounted for 20 percent of the company's revenue, virtually unchanged compared to the year before.
[ Related: Cook Points to China for Apple's Lackluster Q1 | Apple's Services Segment Continues to Grow | Apple's Market Decline In Perspective ]
"How Big Is Apple's China Business?